A Quick Guide to Cloud Data Security in 2025
Reading Time: 4 minutes

Organizations are more and more embracing cloud environments as a storage and processing platform for their data; cloud data security threats will be a major concern in 2025. The accelerated expansion in the usage of cloud services has unlocked an unprecedented level of flexibility and scalability; however, it also grew the space for security, leading to intricate security challenges that need the execution of high-level strategies and best practices to fight and reduce the risk of data breaches and data loss. The following Guide provides a relevant summary of the most significant aspects of cloud data security, including cloud security best practices, hybrid cloud security challenges, common cloud security challenges, data protection best practices, and the creation of an overall cloud security plan.
With data as a key driver of decision-making today, the ability to leverage data effectively is limited for many organizations due to fragmented data storage, isolated systems and limited discoverability. In recent weeks, experts from Sigmoid and Databricks revealed game-changing strategies to democratize data and empower smarter decisions making.
Cloud Security Best Practices in 2025
- Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):Enabling a multi-factor authentication mechanism to include one-time passwords, biometrics, or a physical hardware token are critical layers of verification to minimize the possibility of unauthorized access.
- Using Zero Trust Architecture: A zero trust model assumes that no one is implicitly trusted and frequently validates users and devices to perform healthy access.
- Securing Data In Transit and Data At Rest: Strong data encryption, such as AES‑256, will encrypt data that is at rest and during transportation.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): Fine‑grained, role‑based controls assist securely managing accounts and credentials.
- Continuous Monitoring and Automation: Cloud Security Posture Management tools can quickly, automatically, and continuously identify vulnerable or misconfigured resources and prevent unnecessarily increasing your attack surface.
Hybrid cloud security combines a mix of private and public cloud services that allow organisations to benefit from flexibility, but again, introduces risks unique to hybrid cloud security arrangements:
- Consistent security policies:One of the core aspects of hybrid cloud security is the ability to apply the same policies across all environments, so that security gaps don’t arise.
- Data segmentation and isolation: Data segmentation and isolation is especially critical with sensitive or regulated data, as there will be an increased risk exposure in hybrid security arrangements.
- Secure APIs and Interfaces: As hybrid architectures leverage interconnectivity, secure APIs and interfaces should be a major focus and layered into security strategies.
- Unified visibility: Hybrid clouds are more complex enterprises, but effective visibility enables security teams to detect unauthorized access across ecosystems. By considering hybrid cloud security factors and implementing hybrid cloud security controls and measures, organisations can balance agility and security.
- Cloud Security Challenges:Cloud security also plays a part in the varieties of cloud security challenges. Even as recently as 2025, many of the core cloud security challenges remain.
- Predictable Attack Surfaces :As your resources grow, your organization exposes more entry points to an attacker.
- Identity and Credential Compromise:APsychological human error remains the top contributor for breaches.
- Complexity and Visibility Challenges:This is usually true for an organization that has adopted multi-cloud or hybrid cloud approaches.
- Third-Party Risk:Direct and indirect risk exposure from vendors and partners.
- Rapid Attack Evolution:New threats and attacks occur much faster and sophisticated on a daily basis.
While cloud security challenges can be arduous, continuous assessment, identity security and governance all play important parts in mitigating cloud security challenges.
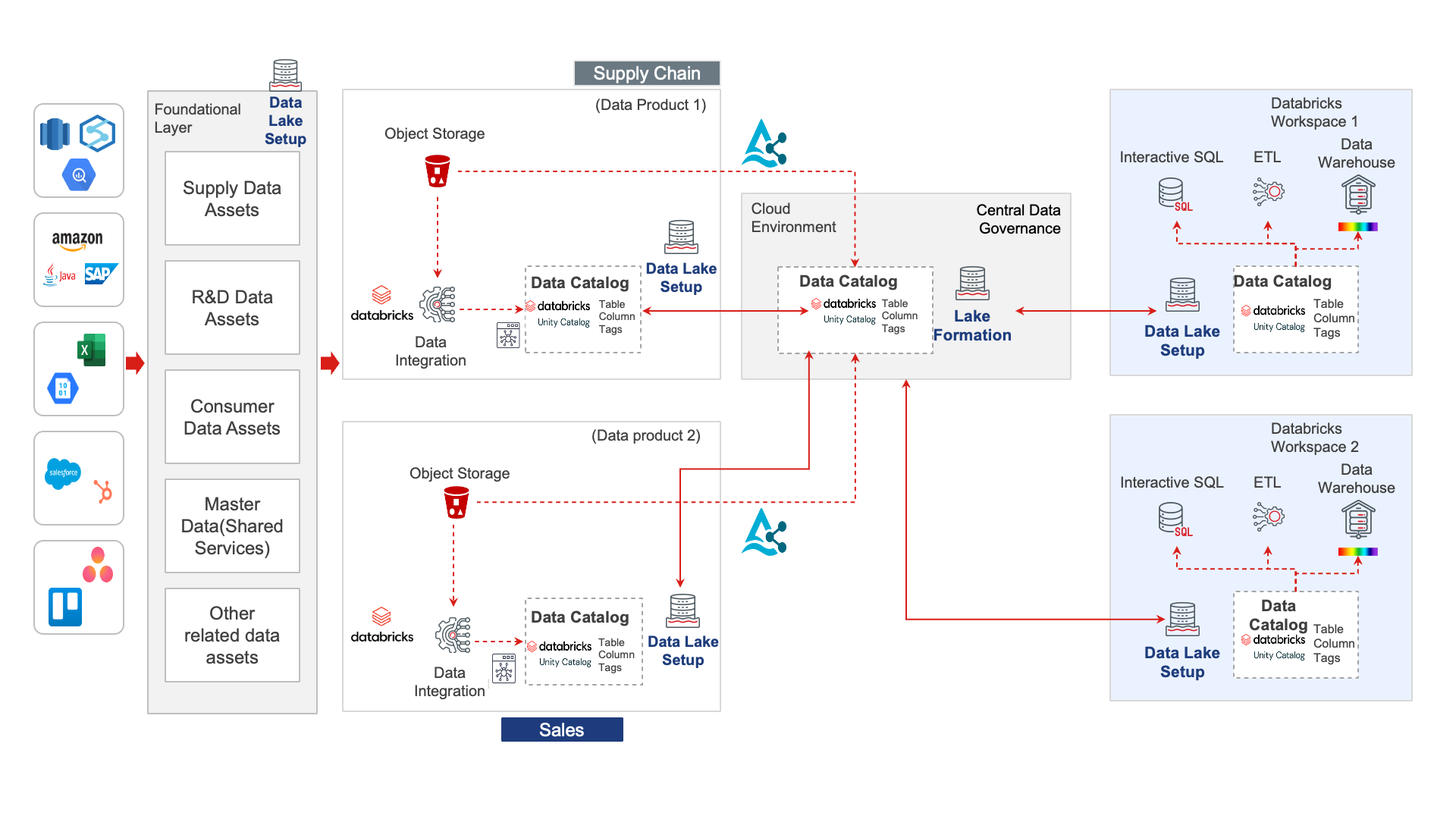
Real-world impact of Data Democratization
Hybrid Cloud Security
Hybrid cloud security combines a mix of private and public cloud services that allow organisations to benefit from flexibility, but again, introduces risks unique to hybrid cloud security arrangements:
- Consistent security policies: One of the core aspects of hybrid cloud security is the ability to apply the same policies across all environments, so that security gaps don’t arise.
- Data segmentation and isolation: Data segmentation and isolation is especially critical with sensitive or regulated data, as there will be an increased risk exposure in hybrid security arrangements.
- Secure APIs and Interfaces: As hybrid architectures leverage interconnectivity, secure APIs and interfaces should be a major focus and layered into security strategies.
- Unified visibility: Hybrid clouds are more complex enterprises, but effective visibility enables security teams to detect unauthorized access across ecosystems.
By considering hybrid cloud security factors and implementing hybrid cloud security controls and measures, organisations can balance agility and security.
- Cloud security also plays a part in the varieties of cloud security challenges. Even as recently as 2025, many of the core cloud security challenges remain:
- Predictable Attack Surfaces: As your resources grow, your organization exposes more entry points to an attacker.
- Identity and Credential Compromise: Psychological human error remains the top contributor for breaches.
- Complexity and Visibility Challenges: This is usually true for an organization that has adopted multi-cloud or hybrid cloud approaches.
-
Third-Party Risk: Direct and indirect risk exposure from vendors and partners.
-
Rapid Attack Evolution: New threats and attacks occur much faster and sophisticated on a daily basis.
While cloud security challenges can be arduous, continuous assessment, identity security and governance all play important parts in mitigating cloud security challenges.
Data Protection Best Practices
Data protection best practices in cloud environments extend well beyond the usual perimeter protections:
- Data Minimization: Only store what you need.
- Encryption and Anonymization: To protect extremely sensitive or personally identifiable data.
- Access Control: Strictly apply least privilege.
- Incident Response Planning: Be ready to respond if things go wrong.
- Employee Training: Teach employees how to handle sensitive data securely.
Compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR is also part of data protection best practices.
Building a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
A well thought out cloud security strategy brings together technology, governance, and people:
- Zero Trust Framework: Continual verification of users and devices.
- Automated Security Tools: CSPM, SIEM, and vulnerability scanning.
- Identity-Centric Security: IAM and MFA front and center.
- Compliance Considerations in the Process: Built into processes from the get-go.
- Security Awareness Culture: Empower staff with training.
Conclusion
By implementing cloud security best practices, mitigating cloud security challenges, applying data protection best practices, securing hybrid cloud security environments, and aligning with a solid cloud security strategy, organizations can confidently utilize the cloud in 2025 without compromising data integrity.

